- How solar battery storage works
- Introduction to solar battery storage
- Tesla Powerwall battery solutions
- What Do Solar Batteries Look Like – and Where Can I Install Them?
- What Size Solar System Should You Have When Adding a Battery
- What’s the Real ROI on Solar and Battery Systems in 2025?
- When are batteries worth it? Solar energy battery viability.
- Which Solar Battery Is Right for Your Home?
- Does Solar Increase Property Value in Shoalhaven? The Numbers Speak for Themselves
- Empowering Small Businesses with Solar: The Australian Small Business Energy Incentive
- How much will you save with solar?
- How the 2025 Australian Cheaper Home Batteries Program Works
- Solar finance options
- The 2024 NSW Government Home Solar Battery Rebate Scheme
- What government incentives and financing options are available for solar?

On-grid vs off-grid solar
While there are three different types of solar power systems (on-grid, off-grid and hybrid), all three work on the same basic principles.
Solar energy or sunlight is first converted by the solar panels into direct current (DC) power, using what is known as the photovoltaic (PV) effect.
This DC power can then either be stored in a battery, or converted by a solar inverter into alternate current (AC) power, which can then be used to run your household appliances.
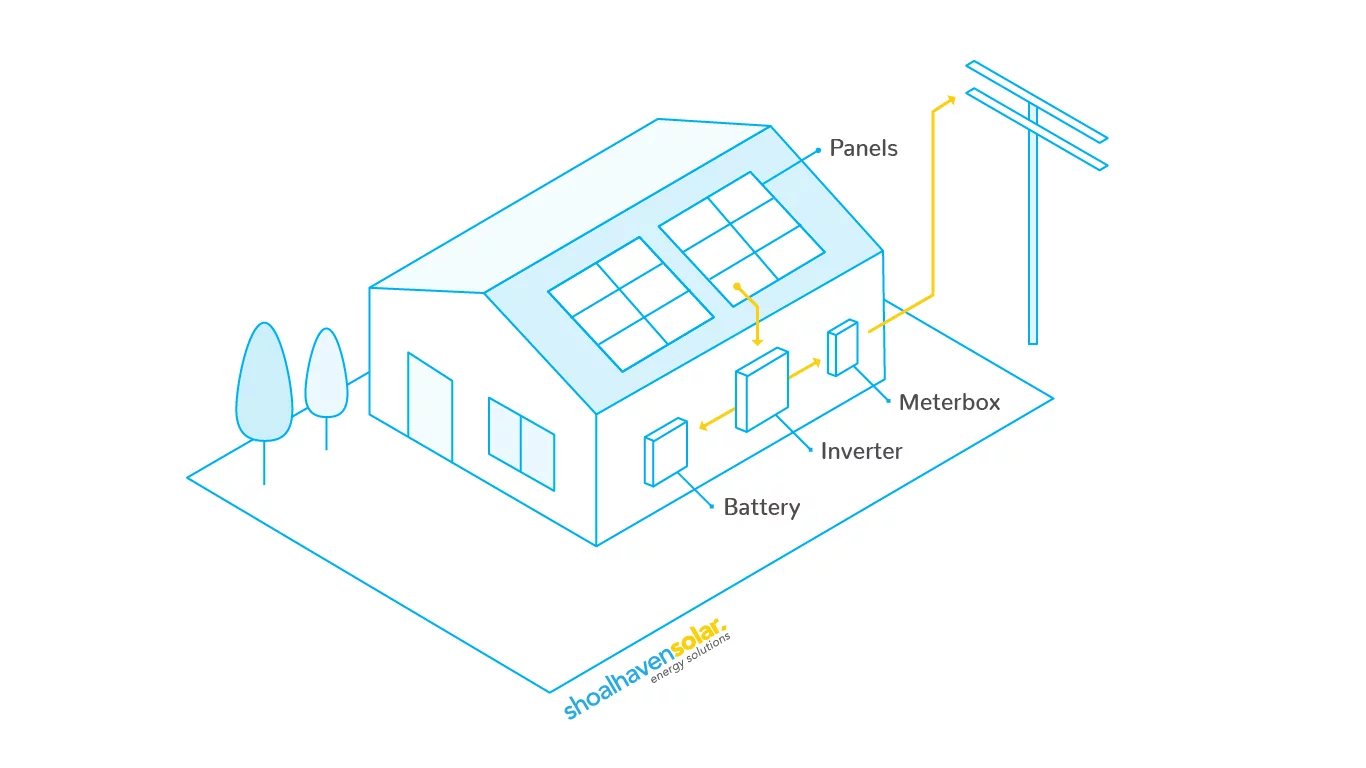
Depending on the type of solar power system being used, excess solar energy can also be fed back into your public electricity grid providing you with credits on your energy account as well as your reduced electricity costs.
In this article, we are going to look at the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of two of the main types of solar power systems currently used Australia-wide:
On-grid solar: also known as a ‘grid-feed’ or ‘grid-tie’ solar system
Off-grid solar: also known as a ‘stand-alone power system’ (SAPS)
On-grid vs off-grid solar: what is the key difference?
The difference between the two solar systems is the ability to store and use excess power that’s been generated by the system.
On-grid solar systems
On-grid is by far the most common and widely used solar systems for homes and business in Australia.
These systems use common solar inverters, are generally placed on top of the roof
But, the main appeal to most people of on-grid solar systems is that they are tied to your local utility’s GRID.
This means that any excess solar power that you generate is exported back into your local electricity grid, allowing you to get paid a ‘feed-in-tariff’ (FiT) or build credits that you can cash out at the end of the year in a process called ‘net metering.
This on-grid system is what most residential homes will use, as you are covered if your solar system either under or over-produces. Basically, your electric utility company acts as your battery space.
Advantages of on-grid systems
You do not have to buy an expensive battery back-up system to store any excess energy, this utility is a 100% efficient battery in itself
You will not need to implement any change to your lifestyle or means of conserving electricity
You will love receiving your credits from your local electricity grid provider for any unused energy that you have generated (on top of already reduced electricity bills!)
Disadvantages of on-grid systems
On-grid solar systems are battery-less and therefore not able to function or generate electricity during a blackout, due to safety reasons. As blackouts usually occur when the electricity grid is damaged – if the solar inverter was still feeding electricity into a damaged grid it would risk the safety of the people repairing the fault/s in the network.
They can’t produce solar energy and reduce your power bill at night-time or when there’s no sunlight.
They provide you with less incentive to conserve energy!
Off-grid solar systems
Off-grid solar systems are not connected to the local electricity grid, and therefore require their own source of battery storage solution, as well as the solar panels and the inverter.
Power that’s generated by the system is used to power the home and appliances, with any leftover power stored in batteries to use of an evening or on a rainy day.
Off-grid systems are often needed in remote areas that are too far away from the local electricity grid, and therefore must be designed to ensure that they will generate enough power throughout the year and have enough battery capacity to meet the requirements of the premises – even in Winter when there is less sunlight.
The additional cost of batteries means that off-grid systems are more expensive than on-grid systems.
However, battery costs are now reducing rapidly which means there is growing enthusiasm for off-grid systems in cities and towns.
Advantages of off-grid solar systems
If on an off-grid system, you are 100% self-sustaining your energy use as you are not connected in any way to your local grid’s power system or utility company
The cost of your energy is predictable, as you can amortize the cost of purchase and installation over the lifetime of the system. A good warranty can mean that without unexpected future costs, the return on investment can be calculated. When you compare this to the often high and fluctuating commercial energy costs, it is an attractive proposition.
These systems are good in terms of expandability as your energy needs change over time
They help prompt you to make efficient use of your electricity, which is good for the environment
Disadvantages of off-grid systems
Off-grid systems require you to purchase a backup battery which can be bulky and expensive
Solar battery systems require regular maintenance
Off-grid options don’t feature the feed-in-tariff as the system is not connected to the grid in any way
So, on-grid vs off-frid: which one is better for me?
If you are located in an area where you are too far to connect to the local electricity supply, or where power supply isn’t reliable, then an off-grid solar system is clearly the best choice available for you.
In most other cases, an on-grid solar system is generally suggested, on the key grounds of both cost-efficiency and reliability.
Especially for residential houses, on-grid solar systems are appealing in that they do not require bulky and costly battery storage solutions, and you will also need fewer solar panels than you would if you were on an off-grid system – due to no need for producing extra power when there is no sunlight.
If you are concerned about future electricity price hikes but don’t want to invest in a battery yet, then a ‘battery-ready’ option which is an on-grid system that can easily be connected to a battery later, may be best for you.
For more advice and information on on-grid vs off-grid solar systems, please contact our friendly sales team today on (02) 4464 1597.